Sentiment and emotion analysis
Sentiment and emotion analysis based on open-ended responses (e.g. in satisfaction surveys or product/service feedback) helps businesses gain a deeper understanding of how customers truly perceive their experiences.
Unlike simple numeric ratings (e.g. 1–5 scores), this type of analysis dives into the content and tone of customer comments—detecting both the general sentiment (positive, negative, or neutral) and specific emotions such as joy, fear, sadness, or trust.
1. Automatic Sentiment and Emotion Detection
Fast Opinion Classification
Automatic analysis lets you instantly classify hundreds or thousands of responses as positive, negative, or neutral.
It provides a quick overview of how respondents perceive your offer or customer service.
Detection of Complex Emotions
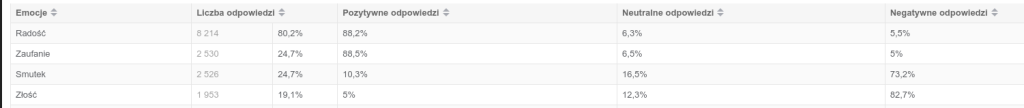
Beyond the standard positive/negative/neutral scale, the system can detect a range of emotions (e.g. Joy, Trust, Fear, Disgust, Anticipation).
This helps capture emotional nuance—not every negative comment reflects anger; it might express disappointment or concern.
Quickly Identify Critical Areas and Opportunities
Sentiment and emotion intensity scores help quickly spot areas that require urgent attention (e.g. many comments expressing Sadness or Anger).
On the flip side, highly enthusiastic feedback (e.g. tagged with Joy or Trust) can be highlighted as positive examples or even used in marketing campaigns.
2. Manual Correction of Automatic Analysis (Sentiment & Emotion Editing)
Fixing Misclassifications
Despite high accuracy, automated algorithms can make mistakes—e.g., misclassifying sarcasm or humor as negative.
Analysts or moderators can manually edit sentiment tags, changing a “negative” label to “positive,” or adding/removing emotions as needed.
Adjusting Confidence and Intensity
The system assigns each detection a confidence score and emotion intensity level.
If an expert believes a comment conveys stronger joy than the algorithm indicates, this can be manually adjusted.
These edits can also serve as feedback for improving the model over time.
Improved Report Accuracy
Final, corrected sentiment/emotion values feed into reports and dashboards, ensuring that aggregated statistics reflect reality as closely as possible.
This results in more reliable insights and better-informed business decisions.
Practical Use Cases
Segmenting Customers by Emotional Tone
You can segment respondents based on their dominant sentiment or emotion, then analyze their answers across other parts of the survey—
e.g., comparing NPS scores for those expressing sadness vs. joy.
Monitoring Trends Over Time
Track whether the volume of negative responses decreases after a service change, or whether trust-related emotions increase.
This helps measure the effectiveness of experience improvements.
Crisis Detection and Response
If a sudden spike in high-intensity negative emotions occurs, the system can alert the team responsible for crisis management.
Marketing Content Creation
Emotion-rich positive feedback (e.g., comments full of Joy or Trust) can be used as customer quotes in marketing materials, social media, or on your website.
Additional Uses of Sentiment and Emotion Analysis
Sentiment and emotion analysis is valuable across many areas of an organization, as it helps deepen the understanding of how customers perceive products, services, and marketing messages.
In customer service, such data supports personalized interactions—allowing agents to adjust tone and communication style based on the customer's emotional state. It also helps prioritize support tickets based on the intensity of negative emotions, ensuring that more urgent issues are addressed faster.
In marketing, insights into dominant audience emotions enable more tailored messaging and allow teams to assess how customers react to specific campaigns or communications. This is particularly effective on social media, where brands can quickly detect sentiment shifts and respond proactively—whether by managing criticism or amplifying positive engagement.
When it comes to brand reputation and online presence, emotion indicators help determine whether the overall brand perception is mostly positive, or whether it needs improvement due to a rising negative tone.
If repeated concerns—such as fear or frustration about a specific feature—start to emerge, the business can take proactive mitigation steps.
Conversely, positive emotions like joy or trust highlight what works especially well and may serve as a foundation for further product or service innovation.
In product development, analyzing emotions enables not only the identification of technical problems but also the detection of more subtle emotional signals like disappointment or resentment, pointing to areas needing improvement.
Responsible Use of Emotional Data
When working with emotional data, it's important to maintain a responsible and ethical approach, especially with sensitive content.
This includes anonymizing responses and securing data to prevent privacy violations.
A best practice is to clearly inform respondents that their comments may be analyzed for sentiment, fostering transparency and trust.
It's also recommended to implement manual correction mechanisms alongside automated sentiment models—so that experts can refine intensity levels or correct misinterpretations.
This helps prevent errors such as sarcastic or humorous comments being misclassified as negative.
Value Beyond Numbers
Ultimately, sentiment and emotion analysis serve as a powerful complement to traditional metrics, offering much deeper insight into user and customer experiences.
Automated algorithms enable the rapid processing of large datasets, while manual editing ensures quality and accuracy.
By combining sentiment results with quantitative data (e.g. satisfaction scores or ticket volumes), businesses gain a holistic view of brand perception—enabling faster reactions to negative feedback and stronger reinforcement of positive messages where there’s potential to spark joy, trust, or enthusiasm.
You can read more in our article on emotion and sentiment analysis.