Manual Categorization of Open-Ended Responses
Manual categorization is the process of assigning individual customer responses to predefined categories.
This method allows for detailed and precise content analysis, giving you full control over the interpretation and classification of the data.
ourCX allows for manual analysis and categorization of open-ended responses.
To access this feature:
Select the survey containing the open-ended responses you want to categorize.
In the left-hand menu, go to “Open-Ended Responses – Manually Assigned Categories”, then choose the question you want to work with.
Click “Responses for Analysis.”
You can apply any filters you need and define a specific time range.
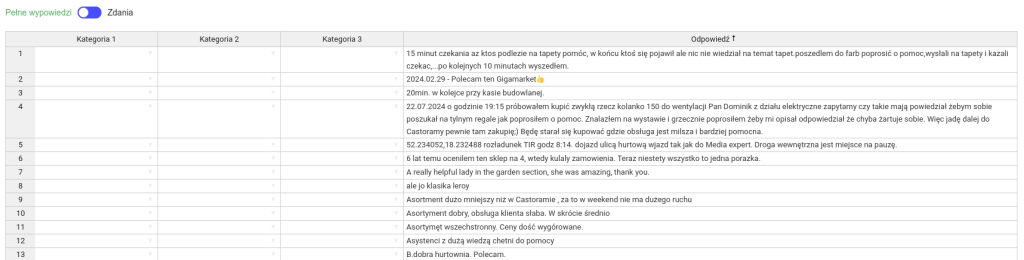
Responses are displayed in an Excel-like interface—each row contains the original open-ended response, and you can assign multiple categories to each one.
You can also choose whether responses are shown in full or split into shorter sentences for easier analysis.
Once categorized, the results will appear under the selected question, including both the percentage share of each category and the number of responses assigned to it.
Why Use Manual Categorization?
Precision and accuracy – manual tagging allows for nuanced interpretation of responses, taking into account context and intent, which improves the quality of analysis.
Custom category creation – users can create and tailor categories to fit the specific needs of their business.
Training data for automated models – manually categorized responses can be used as training data to improve the effectiveness of automatic categorization models.
Flexibility – ideal for smaller datasets or projects that don't require automation.
When to Use Manual Categorization?
Small datasets – such as in qualitative or pilot studies.
When high precision is required – especially for data with high business impact.
Specialized projects – where categories are domain-specific and require expert knowledge.
Training machine learning models – as a reliable base of high-quality labeled data.
Drawbacks of Manual Categorization
Time-consuming
Assigning categories manually is a slow process, particularly for large datasets.
For thousands of responses, the process can take weeks or even months.
Labor costs
Manual categorization often requires multiple analysts, increasing operational costs.
Requires trained professionals, further adding to resource needs.
Subjectivity
Categorization decisions can vary between analysts, leading to inconsistencies.
Interpretations may be influenced by bias or cognitive errors.
Limited scalability
Manual methods are not practical for large-scale or real-time projects.
In dynamic environments requiring fast decisions, this approach is inefficient.
Human error risk
Manual processing increases the chance of oversights or incorrect classifications.
Repetitive tasks can lead to analyst fatigue, reducing accuracy.
Lack of automation
Manual categorization doesn't use algorithms to speed up the process or reduce errors.
It can’t be easily integrated with automated systems without manually creating training sets.
Difficulties with large data volumes
Manually analyzing every entry in a large dataset may be unfeasible.
Highly varied responses make manual classification more difficult.
Limited repeatability
Results may vary if different analysts are involved or if done at different times.
The process lacks easy adaptation and repeatability when requirements change.
Slow response time
In situations where data must be analyzed in real-time (e.g., for quick reporting), manual categorization is impractical.